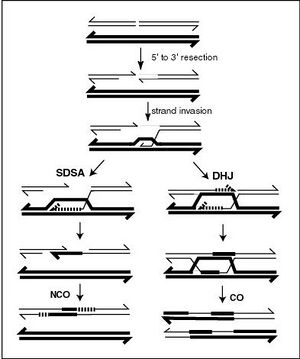
基因重组(genetic recombination)亦称遗传重组(genetic reshuffling),在遗传学上的“重组”是指DNA片段断裂并且转移位置的过程,会导致基因间或基因内新的连锁关系形成。在自然情况下,常发生在减数分裂时非姐妹染色单体上的基因结合。
对原核生物(例如细菌)来说,个体之间可以通过交接,或是经由病毒(例如噬菌体)的传送,来交换彼此的基因,并且利用基因重组,将这些基因组合到本身原有的遗传物质中。
对于较复杂的生物来说,重组通常是因为同源染色体配对时发生互换,使得同源染色体上的基因在遗传到子代时,经常有不完全的连锁。由于重组现象的存在,科学家可以利用重组率来定出基因之间的相对位置,描绘出基因图谱。
联会
在减数分裂期间,联会(同源染色体的配对)通常在基因重组之前发生。在一般减数分裂的步骤,先是联会 、再进行基因重组及分离 (gene segregation)[1][2]。
注释
- ↑ Hawley RS, Arbel T.,"Yeast genetics and the fall of the classical view of meiosis"[1],PubMed - NCBI,1993 Feb 12;72(3):301-3.. PMID 8431941 DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90108-3
- ↑ Peter B. Moens,"Molecular perspectives of chromosome pairing at meiosis"[2],BioEssays - Wiley Online Library,Volume16,Issue2,February 1994,Pages 101-106.
参考文献
![]() 本条目引用的公有领域材料来自NCBI的文档《Science Primer》。
本条目引用的公有领域材料来自NCBI的文档《Science Primer》。
- Michael J. McDonald, Daniel P. Rice, Michael M. Desai: Sex speeds adaptation by altering the dynamics of molecular evolution. In: Nature. 2016, doi:10.1038/nature17143
参见
外部链接
- Animations – homologous recombination: Animations showing several models of homologous recombination
- The Holliday Model of Genetic Recombination
- 医学主题词表(MeSH):Genetic+recombination
- Animated guide to homologous recombination.